A social graph is a visual and mathematical model illustrating the interconnections and relationships among individuals within a social network. These graphs reveal personal bonds, group affiliations, and interactions, forming the backbone of today's major social media platforms. Facebook, for example, has famously maintained the world’s largest and continuously evolving social graph since 2010.
In the realm of credit scoring and fraud detection, social graphs have emerged as powerful tools. They identify hidden relationships and interactions between individuals, significantly enhancing the ability to evaluate potential financial risks or detect fraudulent activities early.
Understanding the Components of Social Graphs
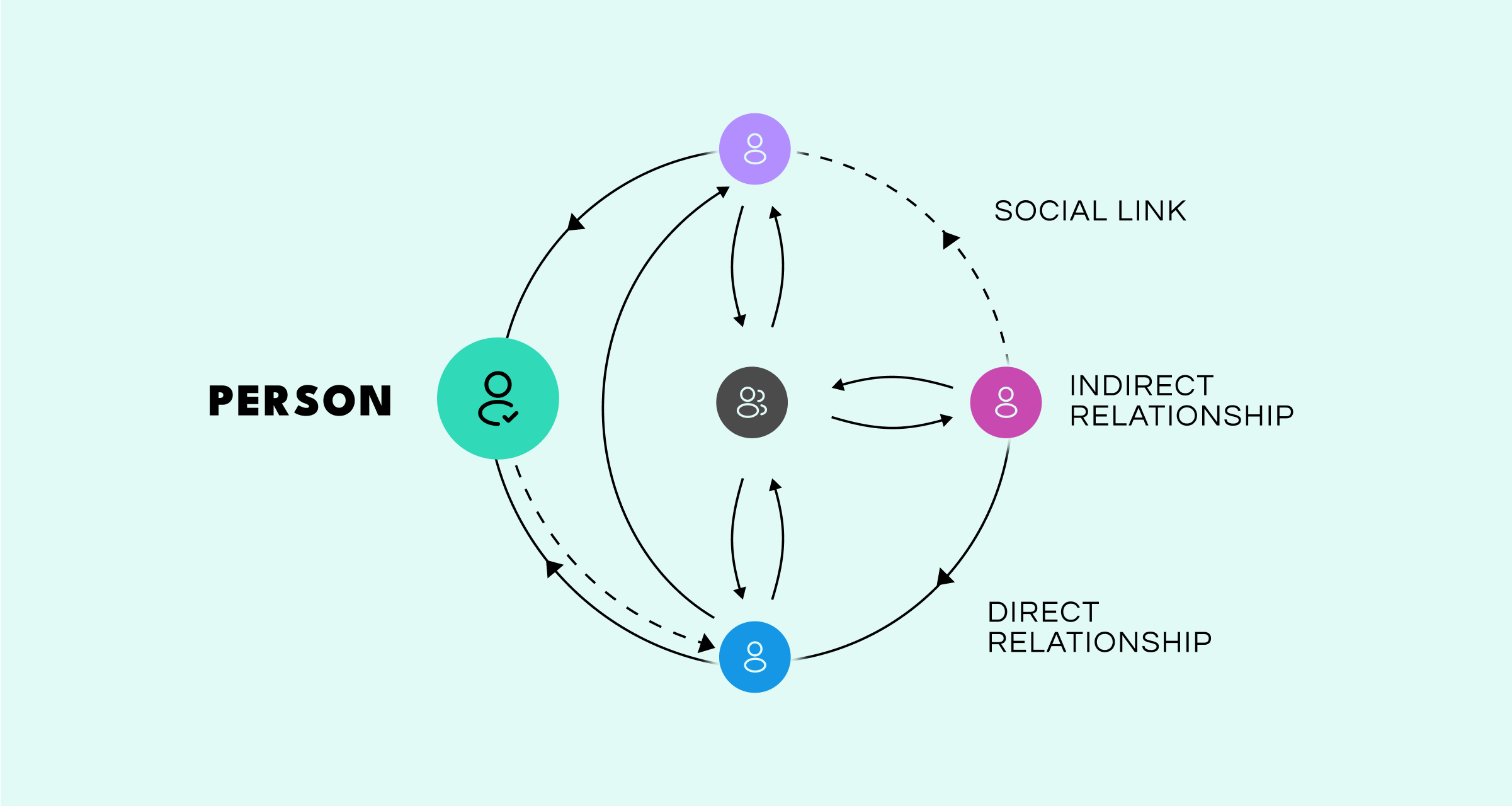
Social graphs typically include three main components:
- Nodes: Represent individuals or entities within the network.
- Edges: Illustrate relationships or connections between nodes, such as friendships or followers.
- Jumping Functions (optional): Capture specific actions or interactions establishing a connection—such as accepting a friend request, liking posts, or sharing content.
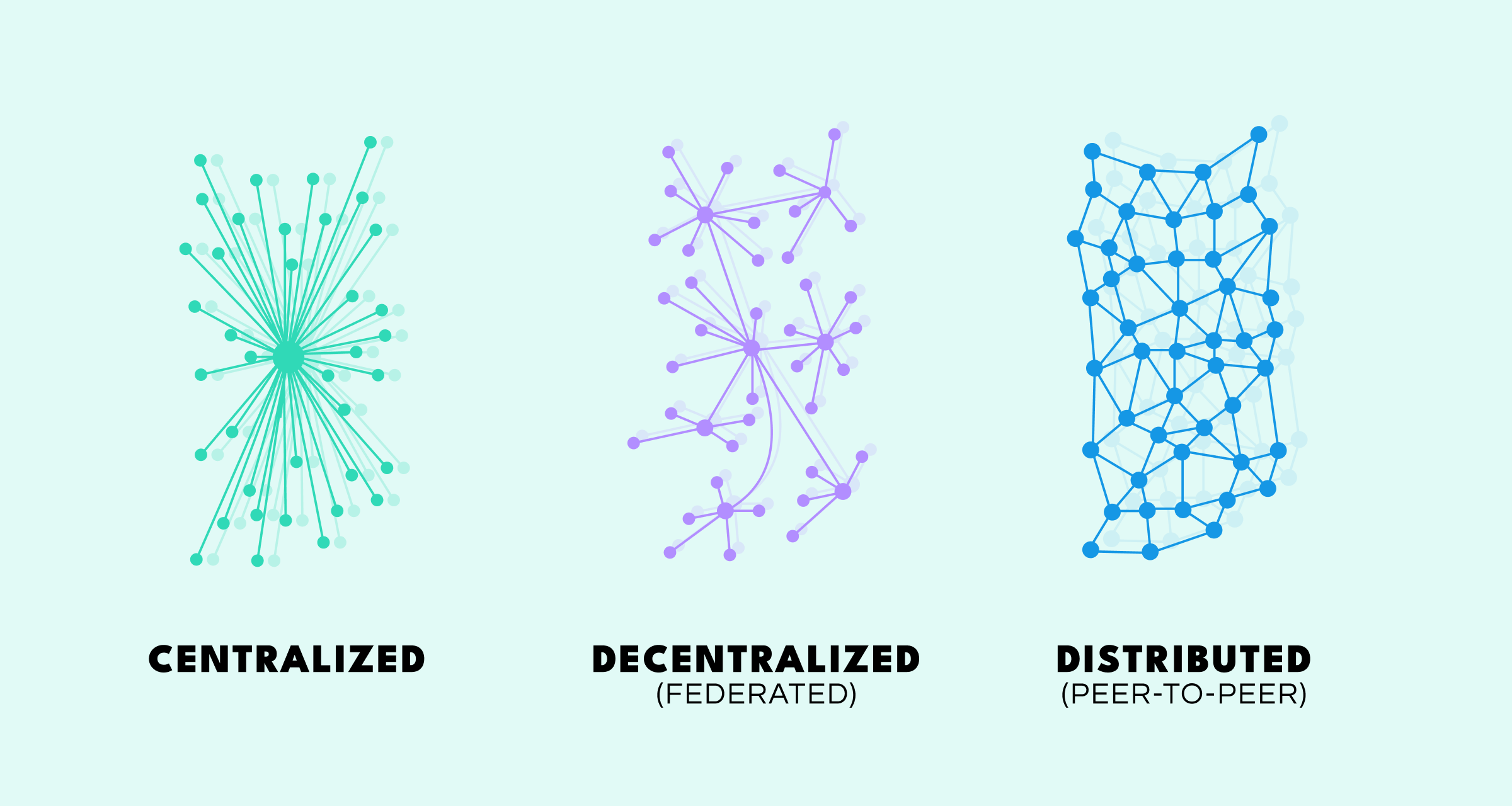
The structure and complexity of social graphs can vary significantly, depending on their intended purpose and the scope of data available:
- Centralized Graph: This structure centers around one primary node, capturing immediate, direct relationships and close social ties.
- Decentralized Graph: Goes deeper by including second-level connections (friends-of-friends) or broader community interests, providing richer insights into larger social structures and indirect relationships.
- Distributed Graph: Illustrates extensive networks without clearly defined group boundaries, highlighting substantial interconnectedness and cohesive community presence.
The Impact of Social Graphs onFraud Prevention and Credit Scoring
Social graphs enhance credit scoring and fraud prevention strategies through several key applications:
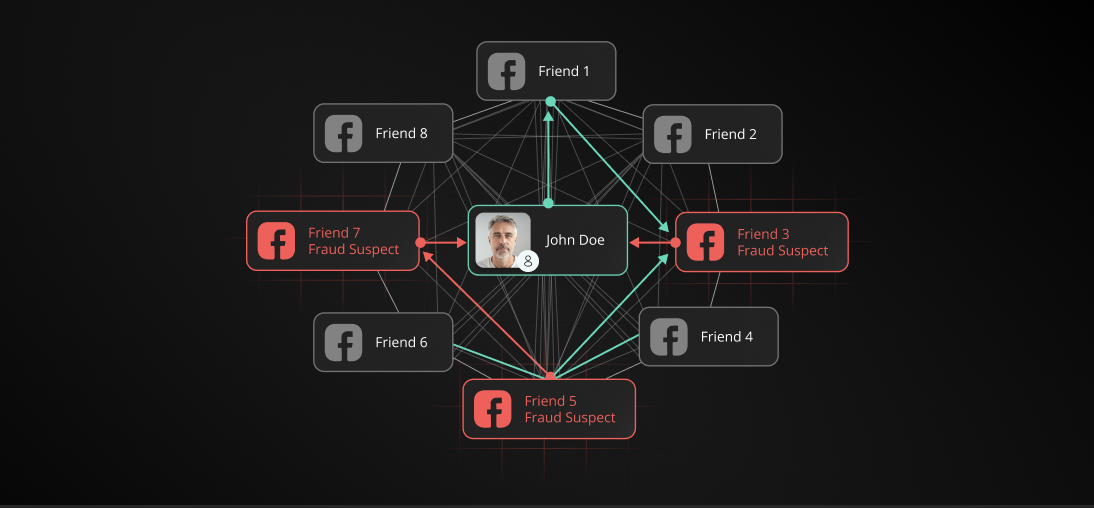
- Fraud Group Detection: Social graphs enable the identification of connections between individuals and known fraudsters, thus highlighting potential fraud risks. Fraudulent actors frequently operate in interconnected groups, amplifying overall credit and financial risk.
- Assessing Friends' Solvency: Examining the financial reliability of an individual's immediate social network offers valuable insights into their own creditworthiness. Multiple connections with financially unstable individuals or known defaulters can indicate higher risk, while a network of financially stable contacts can positively influence credit evaluations.
- Optimizing Marketing and Outreach Campaigns: Financially responsible individuals often have social circles that mirror their own financial habits. Utilizing social graphs, marketers can target these networks more effectively, boosting the success rates of financial products and services.
In conclusion, social graphs provide financial institutions and fintech companies with a sophisticated method to evaluate creditworthiness and detect fraud. By mapping out relationships and interactions, companies can significantly reduce risks, make more accurate credit decisions, and implement more effective marketing strategies.
About Scoreplex
Scoreplex provides alternative data for credit scoring and fraud prevention through digital footprint analysis using over 140 open sources.
By leveraging social media activity analysis, data leak monitoring, social profiling, and dynamic social graph generation, we enhance scoring models with insights that conventional data sources cannot capture.




